- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-13 Origin: Site








You might wonder what is an ‘air change per hour’? This term means how many times fresh air replaces the old air in a room every hour. Experts suggest that aiming for 5 or more air change cycles helps lower the amount of airborne contaminants like viruses.
Air change per hour measures how often you get new air in your space.
More air changes help keep indoor air cleaner and safer.
Performance Impact (%) | |
|---|---|
650 | Baseline |
950 | -15 |
1500 | -50 |
22 CFM/person | +26 |
17 CFM/person | Baseline |
You can use air change rates to improve air quality at home, work, or in public areas.
Air change per hour (ACH) shows how often new air comes in. It pushes out old air from a room. Try to get at least 5 ACH for cleaner air.
More ACH means less dust and fewer germs in the air. This makes it safer to breathe inside.
To find ACH, use this formula: ACH = (Airflow Rate in CFM x 60) / Room Volume in cubic feet.
Good airflow lowers CO2 levels. This helps you focus better and feel healthier.
Open windows and use fans to let in more fresh air. This raises ACH and does not cost extra money.
At work, try for 2 to 6 ACH. This keeps the air healthy, especially when people get sick more often.
Ask HVAC experts for help if your ACH is low. They can help make your air cleaner and safer.
Check your ventilation system often. Make sure it meets the ACH standards you need.
You may ask, what is an ‘air change per hour’? This term describes how many times the air in a room gets replaced with fresh or filtered air every hour. In building science, experts call this the air exchange rate. When you see a higher number for air changes per hour, it means the air in your space gets refreshed more often. You can think of it as a cycle where old air leaves and new air comes in. This process helps keep the air you breathe cleaner.
Air changes per hour measure how many times the full volume of air in a room is added, removed, or exchanged with clean air. If you picture a classroom or your living room, imagine all the air inside being swapped out several times each hour. This number gives you a clear idea of how well your space stays ventilated.
Tip: If you want to improve the air in your home or office, start by checking how many air changes per hour your space gets.
You might wonder why air change is so important. The answer is simple: it helps protect your health and comfort. When you have enough air changes per hour, you lower the amount of dust, germs, and other pollutants in the air. This makes the air safer to breathe.
Ventilation helps to dilute indoor-generated air pollutants and expel them from buildings, which is crucial for maintaining air quality.
Higher indoor CO2 levels, resulting from human activity, indicate insufficient ventilation, as they are typically higher than outdoor levels.
Increased indoor CO2 concentrations correlate with lower air quality ratings, more acute health symptoms, and diminished cognitive performance.
If you do not have enough air change, you may notice the air feels stuffy or stale. You might feel tired or have trouble focusing. In places where people gather, like schools or offices, good air changes per hour can help everyone feel better and work smarter. You also reduce the risk of spreading illnesses when the air gets replaced often.
What is an ‘air change per hour’? It is a simple way to measure how fresh your indoor air stays. By understanding and improving this number, you can create a healthier and more comfortable space for yourself and others.
When you look at air change per hour, you see how much air gets swapped out in a room. This measurement tells you the total volume of air that leaves and gets replaced with fresh air. If you have a large room, you need more air to keep things fresh. Small rooms need less, but the process works the same way. You can picture it like refilling a fish tank with clean water. The more often you refill, the cleaner the tank stays.
Air change also shows how often this replacement happens. If your space gets six air changes per hour, the air inside gets refreshed six times every hour. This steady exchange helps keep the air from getting stale. You feel the difference when the air moves regularly. Stuffy rooms often have low air change rates.
Proper air change helps control many unwanted things in the air. You can reduce:
Gases, such as carbon dioxide or odors
Hazardous materials, including germs and chemicals
When you keep the air moving, you lower the risk of breathing in these contaminants.
Note: The most common ways to measure air change per hour include direct measurement with tools like anemometers and the tracer gas method, which tracks how quickly a gas disappears from the room.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Direct Measurement | Measures air flows using instruments at exhaust and supply points. |
Tracer Gas Method | Uses a tracer gas to track how fast its concentration drops over time. |
Air change per hour gives you a clear sign of how well your ventilation system works. If the number is high, your system replaces air quickly. This means you get better air quality and a safer environment. In places like cleanrooms or labs, high air change rates are crucial for keeping the space free from harmful particles.
Air change per hour shows how many times the air in your space gets replaced in one hour.
This number helps you judge how well your system keeps the air clean and safe.
You want enough air change to keep the air fresh, but not so much that you feel cold or uncomfortable. Good ventilation balances air change with comfort. If the system works too hard, you might notice drafts or noise. If it works too little, the air feels stuffy. Temperature and humidity also play a role. When air change interacts with these factors, the effect is not always simple. Sometimes, changes in temperature or humidity can make the air feel better or worse, even if the air change rate stays the same.
Parameter Interaction | Significance | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|
p<0.05 | Non-linear (edf>2) | |
Throughput | edf=4.1; p=0.00093 | Significant |
Air change per hour is helpful, but it does not tell the whole story. You need to know its limits:
ACH does not consider how many people are in the room. More people mean more risk, even if the air change rate is high.
If you double the room size but keep the same clean air delivery, the ACH drops. This can make the space seem less safe, even if the air is still clean.
Small, crowded rooms can have high ACH numbers, but not enough airflow for everyone. The risk stays high.
You should use air change along with other measures to get the best picture of indoor air quality.
You can calculate air changes per hour using a simple formula. This formula helps you see how often the air in your room gets replaced. The steps are easy to follow:
Find the airflow rate in cubic feet per minute (CFM) for your ventilation system.
Measure the volume of your room in cubic feet.
Multiply the airflow rate by 60 to get cubic feet per hour.
Divide that number by the room volume.
The formula looks like this:
ACH = (Airflow Rate in CFM x 60) / Room Volume in cubic feet
This calculation gives you the number of times the air changes in your space every hour.
To calculate air changes, you need to know your room’s volume. Measure the length, width, and height of the room. Multiply these numbers together to get the total volume in cubic feet. For rooms with unusual shapes, break the space into smaller sections, measure each, and add the volumes together.
Tip: Use a tape measure for accuracy. Write down each measurement before you multiply.
You also need the airflow rate. You can find this number in your HVAC system’s manual or ask a professional. Some people use an anemometer to measure airflow at vents. If you use a portable air cleaner, check the manufacturer’s specifications for CFM.
Let’s say your room is 10 feet wide, 15 feet long, and 8 feet high. The volume is:
10 x 15 x 8 = 1,200 cubic feet
Your ventilation system delivers 200 CFM. Multiply by 60 to get 12,000 cubic feet per hour. Divide by the room volume:
ACH = 12,000 / 1,200 = 10
You have 10 air changes per hour in this room.
Room shape and size change how you calculate air changes per hour. Large rooms need more airflow to reach the same ACH as small rooms. Odd shapes may require you to measure each part separately.
Furniture and walls can block airflow. When air cannot move freely, some areas may not get enough fresh air. Studies show that the path between air sources and exhausts matters more than just the ACH number. Good airflow distribution keeps the whole room safe.
The performance of your HVAC system affects how well you calculate air changes per hour. Systems that bring in more outdoor air improve air quality. Seasonal changes can also impact how much air your system moves. In summer, ACH often increases because systems run longer.
Open doors and windows let more air in and out. This can raise the ACH, especially if outdoor air quality is good. If you close them, the ACH drops, and the air may feel stale.
The number of people in a room changes how you calculate air changes. More people need more fresh air. Activities like cooking or exercising also increase the need for higher ACH. Different spaces, such as homes or workplaces, have unique requirements.
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
More people need higher ACH for comfort and safety. | |
Room Layout | Walls and furniture affect airflow distribution. |
Performance and settings change ACH throughout the year. | |
Openings | Doors and windows impact how much air enters or leaves. |
Activities | Cooking, cleaning, or exercise increase the need for fresh air. |
Note: Always check your space for things that block airflow. Adjust your ventilation system or move furniture to help air move better.
By learning how to calculate air changes per hour and understanding these factors, you can keep your indoor air fresh and healthy.
You might ask, what does ‘air change per hour’ mean? It shows how often new air comes into your room. More air changes help get rid of things like dust and carbon dioxide. They also remove tiny particles from the air. During the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists studied air quality in big rooms. They checked CO2 and aerosol levels. They found that more air changes meant less pollution. Cheap sensors helped track these changes over time.
Scientists watched CO2 and dust in a lecture hall.
More air changes made the air cleaner inside.
Sensors measured pollution for many hours.
Here is a table with the results:
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
CO2 concentration reduction | 946 and 944 ppm |
Average increase in CO2 | 95 ppm and 100 ppm per hour |
Air exchange rate | 14% |
CO2 removal efficiency | 34% |
So, when you hear about ‘air change per hour’, remember it helps keep your air clean and healthy.
Clean air does more than remove dust or smells. It helps you feel good and stay healthy. Studies show air changes per hour can change how you feel in a room. The right air change slows down germs and viruses. Other studies found fewer infections and less stress in hospitals with good air changes.
Study | Findings |
|---|---|
Kameel and Khalil | HVAC supply air temperature and humidity can slow bacteria and affect viruses. |
Lutz et al | |
Rashid and Zimring | Made a plan to connect indoor air with patient stress. |
Ulrich et al | Studied how building features affect patient recovery. |
Better air changes per hour help everyone breathe easier. People can focus, relax, and get better faster.
Some places need more air changes to stay safe. Hospitals and labs use high air change rates to protect people. These places have more germs and chemicals. Most hospitals use 20 to 25 air changes per hour. Some states say you need at least 15 or 20, depending on the rules.
Ventilation Rate (ACH) | Context | Implication |
|---|---|---|
4 to 12 | General laboratories | Used before, but not always enough |
< 6 | Low-hazard laboratories | Lower rates need careful checks |
20 to 25 | Hospitals | Helps control infections |
15 or 20 | Minimum requirement | Depends on state rules |
Note: Even with lots of air changes, some risks stay. Hospitals sometimes use up to 40 air changes per hour to lower infection chances.
Air change is not just for comfort. It is very important for safety, especially where there are more risks.
You spend a lot of time at home. That is why indoor air quality is important. Most homes have an air change rate between 0.35 and 1 per hour. This means fresh air comes in less than once every hour. Experts like ASHRAE and the EPA say you should have at least 0.35 air changes per hour. This helps get rid of indoor pollutants and keeps your home healthy. If you open windows or use exhaust fans, you can raise the air change rate. Homes with good ventilation feel fresher and safer. Studies show most homes reach about 0.5 air changes per hour. This helps lower harmful emissions and makes the air better.
Tip: You can make air better by checking your ventilation system and opening windows when you can.
You might work or study in offices, schools, or other shared spaces. These places need more air changes than homes because more people share the air. The best rate depends on how many people are there and how big the room is. Offices and classrooms usually aim for 2 to 6 air changes per hour. When viruses spread more, experts say to raise the rate to 6-12. This helps remove germs and keeps everyone safer.
Space Type | Typical ACH Range | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Office | 2 - 6 | Cuts down CO2 and odors |
Classroom | 3 - 6 | Lowers germs and dust |
High-risk (virus season) | 6 - 12 | Extra protection for health |
Note: More air changes mean cleaner air and less chance for sickness to spread.
Hospitals and labs need the highest air change rates. These places deal with germs, chemicals, and other dangers. Air change rates go from 6 up to 12 or more per hour, depending on the room’s job. For example, autopsy rooms and soiled workrooms need even higher rates to control smells and keep people safe. High air change rates help stop infections from spreading and protect workers and patients.
Area designation | Minimum total air change per hour | Implications for infection control |
|---|---|---|
General | 6 | High air changes help lower airborne germs. |
Biochemistry | 6 | Keeps the area safe for handling samples. |
Microbiology | 6 | Very important for stopping contamination. |
Autopsy room | 12 | Needed for controlling smells and germs. |
Soiled workroom | 10 | Lowers risk of infection from dirty materials. |
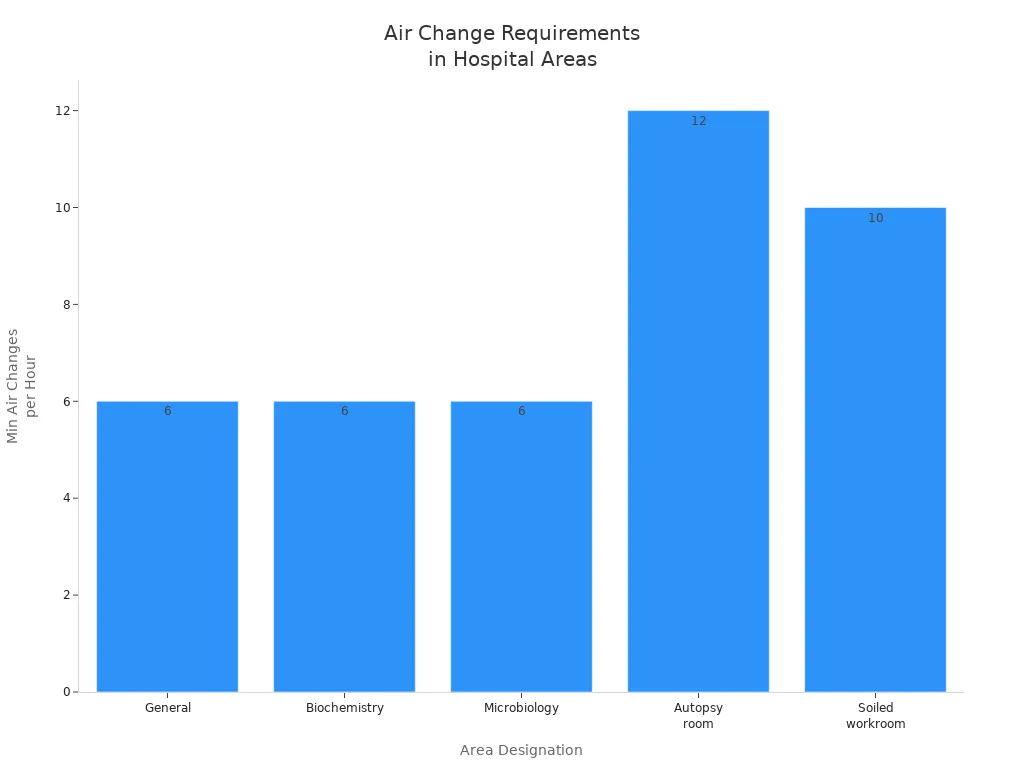
Hospitals use high air change rates to keep patients and staff safe from infections.
You can see that air change rates are different for each place. Homes need enough to keep air fresh. Workplaces need more to protect groups. Hospitals and labs use the highest rates for safety.

Start by finding out your current air change per hour. Measure the airflow from your vents. Figure out your room’s size. Use the formula from earlier in this blog. Write down what you find. If your ACH is low, the air may feel stale. You might also smell odors that do not go away. High ACH means the air is fresher and has fewer bad things in it. Checking often helps you find problems early.
Tip: Try a simple airflow meter or ask your HVAC technician for help. Keeping notes lets you see if things change over time.
There are many ways to get more air changes in your space. Some work best at home. Others are better for offices or big buildings.
Open windows and doors to let in fresh air. Cross-ventilation works best if you open windows on both sides of a room. Fans can help move air outside. Natural ventilation does not cost much and uses no extra energy. But outdoor air and weather can change how well it works.
Open windows for at least 10 minutes every hour.
Use window fans to bring air in or push it out.
Move furniture so it does not block the air.
Mechanical ventilation uses fans, HVAC systems, or air purifiers. These can quickly raise your ACH. You can change settings to get more airflow. Some buildings use special systems to control how air moves.
Ventilation Type | |
|---|---|
Positive Pressure (High) | 94% |
Negative Pressure (Low) | 62% |
Upgrading your HVAC system can give you more ACH, but it costs more money. New rules, like ASHRAE 241, want buildings to double or triple their ACH. This means you pay more for equipment and labor. Your energy bills may go up if you run systems longer. In the last ten years, electricity prices have gone up about 80%. You need to think about getting better air and paying more.
Study | Findings |
|---|---|
Li (2012) | Using energy in buildings adds to CO2 emissions. |
Spandagos et al. (2021) | Buildings use 40% of U.S. energy and greenhouse gases. |
Wongwuttanasatian et al. (2015) | Air conditioning uses a lot of a building’s energy. |
Note: More air changes mean cleaner air, but you will use more energy and spend more money.
Call an HVAC or indoor air quality expert if you cannot get the right ACH. You should also call if you have health problems like headaches or allergies. Experts can measure your air change rate and tell you how to fix it. They know how to solve air quality problems and make your space safer. Paying for help can keep you from getting sick from bad air. Experts use special tools and know-how to find hidden problems and give you the best answers.
If you want a healthy and comfortable home, getting help from a pro can really help.
You may ask how many air changes per hour you need. Experts give advice to help keep air clean and safe. Groups like ASHRAE and the CDC set numbers for hospitals and other places. These numbers show the least amount of fresh air you should get each hour.
Here is a table with some examples:
Building Type | ASHRAE Minimum Total ACH | |
|---|---|---|
Critical and Intensive Care | 2 | 6 |
Airborne Infection Isolation Room | 2 | 12 |
Examination Room | 2 | 6 |
ASHRAE and the CDC say rooms that fight airborne infections need 6-12 air changes per hour. Hospitals and clinics use these numbers. Most homes and offices have lower air changes, but you still need enough to keep air fresh.
Tip: Always look at the rules for your building type. Some places need more air changes to keep people safe from germs or chemicals.
You must follow rules to meet these standards. Building codes and guidelines help make sure your ventilation works well. ASHRAE Standard 62.1 sets the lowest ventilation rates for most buildings. ASHRAE Standard 62.2 gives rules for homes and small buildings. These standards help keep indoor air safe.
Standard | Description |
|---|---|
62.1 | Sets lowest ventilation rates and ways to keep indoor air quality (IAQ) good and lower health risks. |
62.2 | Gives rules for designing ventilation and keeping IAQ good, so you meet the lowest air change standards. |
You need to keep your ventilation system on when people are inside. Only turn it off for repairs or emergencies. This keeps air clean all day.
Make sure your HVAC system runs during business hours.
Check your system often to see if it meets the needed air change rates.
Fix problems fast to keep everyone safe.
Note: Following these rules helps protect your health and others’ health. Good ventilation is not just a rule—it makes your space safer and more comfortable.
You help keep the air inside healthy. Air change per hour affects how safe and comfortable you feel. The CDC says you need at least 5 air exchanges each hour in places people use. You can turn your thermostat fan to 'on' to move air better. Change filters often to keep air clean.
Environment Type | Minimum ACPH | Importance |
|---|---|---|
ISO Class 7 | 30 | Keeps air clean for important work |
ISO Class 8 | 20 | Lowers the chance of contamination |
Anterooms | 60 | Makes particle-generating jobs safer |
Check your HVAC system often. Teach others about air quality. Act fast if you notice air problems. Fresh air helps you feel good and stay safe every day.
ACH means Air Changes Per Hour. You use it to measure how many times fresh air replaces old air in a room every hour.
You can measure your room’s ACH by finding the airflow rate and room volume. Use the formula:ACH = (Airflow Rate in CFM x 60) / Room Volume in cubic feet
ACH helps you keep your air clean. You lower dust, germs, and odors. You feel better and stay healthier when you have enough air changes.
Yes! Opening windows lets more fresh air in. You boost your ACH and improve air quality, especially if outdoor air is clean.
Experts suggest 3 to 6 air changes per hour for classrooms. This helps students and teachers breathe easier and stay focused.
Higher ACH can raise energy use. Your HVAC system works harder to move more air. You may see higher bills if you increase ACH.
You should contact an HVAC or indoor air quality professional. They can test your system and help you improve your ACH for better health.
Low ACH means stale air stays longer. You may notice more odors, feel tired, or get sick more often. Fresh air helps you stay comfortable and safe.